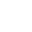
1. Process Overview
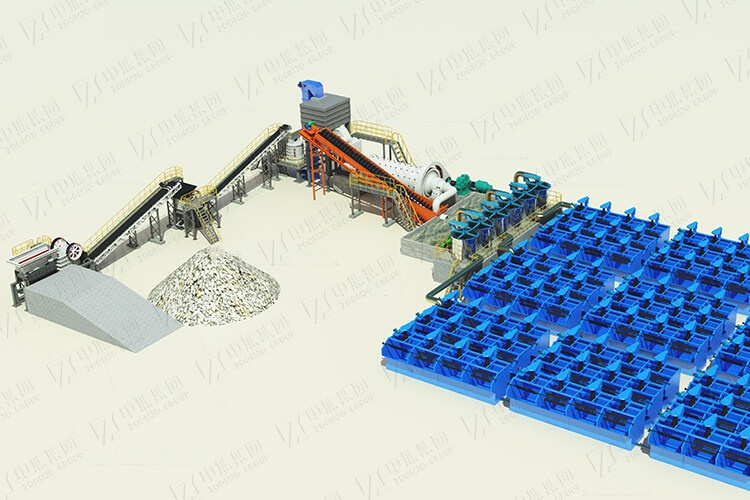
The lead-zinc ore dressing process uses priority flotation and mixed flotation as the core process. In view of the differences between sulfide ores and oxide ores, it combines gravity separation, magnetic separation, and flotation to achieve efficient separation of lead and zinc and comprehensive recovery of associated minerals (silver, sulfur, fluorite, etc.). ZOOMJO GROUP's customized solution can handle complex polymetallic ore bodies, with a comprehensive lead and zinc recovery rate of over 85%, and a concentrate grade of >45%, taking into account both economic and environmental performance.

2. Applicable ore body characteristics
Sulfide ore: mainly galena (PbS) and sphalerite (ZnS), with associated pyrite and silver minerals, and uneven distribution of particle size.
Oxide ore: mainly cerussite (PbCO₃) and smithsonite (ZnCO₃), with high mud content and poor floatability.
Complex paragenetic ore: lead and zinc coexist with multiple components such as copper, silver, sulfur, and barite, requiring multiple processes for coordinated sorting.
3. Core process flow
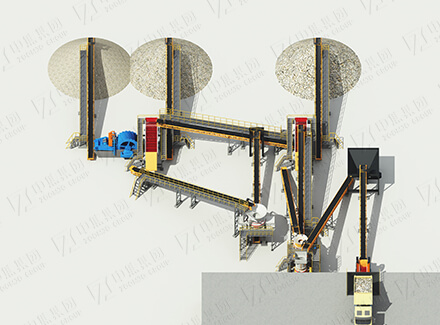
1. Crushing and grinding
Three-stage one closed-circuit crushing: jaw crusher + cone crusher combined, output -12mm particle size, crushing energy consumption reduced by 25%;
Stage grinding:
First stage ball mill (-0.3mm) → lead roughing and tailing;
Second stage ball mill (-0.074mm accounting for 80%) → zinc flotation and dissociation.
2. Flotation separation
Sulfide ore is preferentially floated:
Lead flotation:
Zinc suppression and lead flotation: lime slurry (pH 9-10), zinc sulfate + cyanide suppress sphalerite;
Collector: ethyl thiourea/black medicine targeted adsorption of galena, lead grade of crude concentrate is >50%.
Zinc flotation:
Copper sulfate activates sphalerite, xanthate collector, zinc grade of concentrate is >45%.
Oxide ore combined process:
Sulfidation conversion flotation (Na₂S activation) + gravity pre-enrichment (shaking table/spiral chute), the recovery rate is increased to 70%-80%.
3. Recovery of associated minerals
Silver recovery: Silver minerals are enriched with lead concentrate, and the silver content of lead concentrate is >200g/t;
Sulfur recovery: Flotation tailings strong magnetic separation/refloatation, sulfur concentrate grade >35%;
Fluorite purification: Flotation tailings acid leaching (H₂SO₄) + flotation, CaF₂ grade >85%.

4. Dehydration and environmental protection
Dehydration of concentrate:
Lead and zinc concentrates are concentrated separately → Chamber filter press (water content <12%);
Tailings treatment:
Dry discharge process: cyclone + dewatering screen, tailings water content <15%, water return rate ≥90%;
Wastewater resource utilization: neutralization sedimentation + membrane filtration, heavy metal removal rate >99%.
4. Technical advantages and benefits
High sorting accuracy:
Lead-zinc mutual content <3%, silver comprehensive recovery rate >75%;
Sulfide ore lead and zinc recovery rates reach 90% and 88% respectively.
Cost optimization:
Stage grinding reduces over-grinding and reduces electricity consumption per ton of ore by 30%;
New environmentally friendly reagents (low cyanide/cyanide-free) save 20% of costs.
Green production:
Tailings are used to make building materials (bricks, cement), with a resource utilization rate of >40%; wastewater "zero discharge" system, in line with GB 25467 standards.

5. Typical case: A complex lead-zinc mine project in Yunnan (2000t/d)
Ore characteristics:
Lead 2.1%, zinc 3.5%, silver 65g/t, contains sulfur and fluorite, oxidation rate 30%.
Process plan:
Sulfide ore section: lead floatation first → zinc-sulfur mixed floatation → zinc-sulfur separation;
Oxidation ore section: gravity pre-enrichment → sulfide flotation;
Associated product recovery: tailings flotation fluorite + magnetic separation of pyrite.
Results comparison:
| Indicators | Ore grade | Concentrate grade | Recovery rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead (%) | 2.1 | 58.2 | 91.3 |
| Zinc (%) | 3.5 | 49.8 | 87.6 |
| Silver (g/t) | 65 | 285 | 82.4 |
| Sulfur (%) | 12.5 | 38.7 | 68.9 |




 English
English
 中文
中文