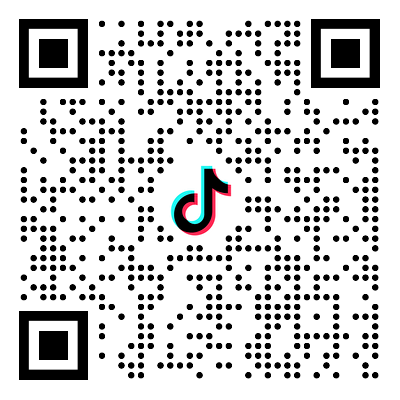
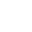
1. System Overview
The flotation process is the core technology for mineral separation, covering the separation of more than 95% of non-ferrous metal minerals and some ferrous metals, precious metals, and non-metallic minerals, and is widely used in the efficient extraction of copper, lead, zinc, iron, graphite and other minerals. The separation of target minerals and gangue is achieved through reagent regulation and bubble adsorption, which is suitable for the particle size range of 0.074-0.4mm, and the concentrate recovery rate can reach 85-98%, and the tailings grade is reduced by 30-70%.
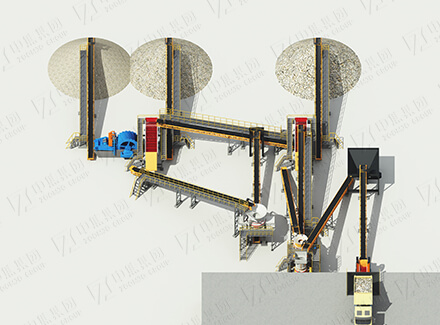
2. Core Process System
Pretreatment system
| Equipment | Function | Technical parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Jaw crusher | Coarse crushing to ≤300mm | Processing capacity 50-1500t/h |
| Cone crusher | Medium crushing to ≤20mm | Hydraulic adjustment of discharge port ±1mm |
| Ball mill | Fine grinding to 0.074-0.4mm | Installed power 200-5000kW |
| Spiral classifier | Particle size classification and desludging | Grading efficiency ≥85% |
Flotation Module
Flotation machine type:
Mechanical stirring type
Aerated type
Pharmaceutical system:
| Agent type | Function | Typical dosage (g/t) |
|---|---|---|
| Collector (xanthate) | Selectively adsorb target minerals | 50 - 200 |
| Frother (pine oil) | Stabilize bubble structure | 10 - 50 |
| Inhibitor (lime) | Inhibit gangue minerals | 500 - 2000 |
Aftertreatment system
Concentration and dehydration: high-efficiency thickener (underflow concentration ≥ 65%) → plate and frame filter press (water content ≤ 15%)
Drying and packaging: rotary dryer (hot air temperature 150-300℃) → automatic ton bag packaging system
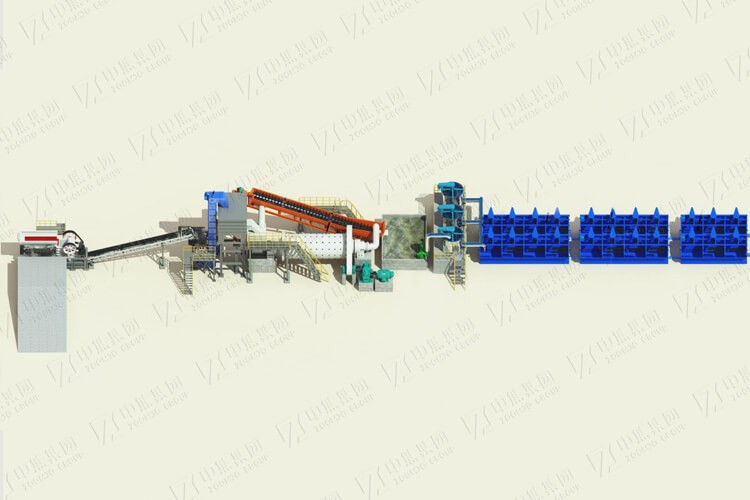

3. Comparison of flotation process types
| Process type | Applicable scenarios | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Priority flotation | High-grade coarse-grained minerals (such as copper sulfide ores) | 工Stable process and easy-to-control indicators | Many equipment requirements and high costs |
| Bulk flotation | Low-grade polymetallic ores (such as lead-zinc paragenetic ores) | Rough grinding and discarding to reduce subsequent costs | Difficulty in separation, and the influence of residual drugs |
| Partial bulk flotation | The floatability of multiple minerals varies significantly (such as copper-molybdenum-sulfur ore) | Step-by-step optimization of recovery | The process is complex and difficult to control |
| Equal flotation | Complex interbedded polymetallic ores (such as tungsten-tin fine mud) | Small dosage and high selectivity | Large equipment investment |
4. Typical mineral flotation process
Copper ore flotation
Sulfide copper ore: priority flotation (xanthate + lime), concentrate grade ≥ 25%, recovery rate ≥ 90%
Oxide copper ore: sulfide-flotation (Na₂S activation), concentrate Cu ≥ 18%, recovery rate ≥ 80%

Lead-zinc ore flotation
Priority flotation process: zinc suppression lead flotation (zinc sulfate + cyanide) → activated zinc flotation (copper sulfate)
Separation index: Pb ≥ 55%, Zn ≥ 45%, comprehensive recovery rate ≥ 85%

Iron ore flotation
Direct flotation: oleic acid collector, concentrate TFe≥65%
Reverse flotation: amine collector quartz, concentrate SiO₂≤4%

Graphite flotation
Multi-stage grinding: 9-stage grinding + 10-stage flotation, fixed carbon ≥ 92%, recovery rate ≥ 87%
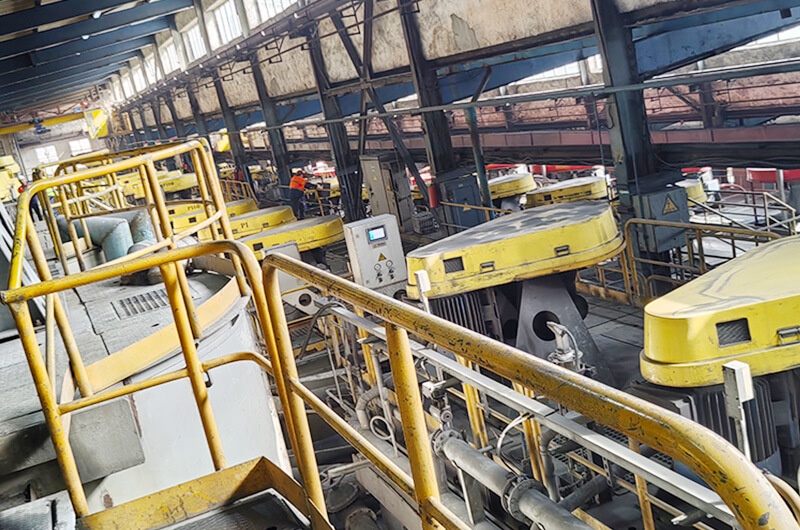

5. Technical parameters and cases
| Cases | Vietnam graphite mine | Indian feldspar ore | Philippine iron ore |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processing capacity | 100 TPH | 125 TPH | 150 TPH |
| Ore grade | Fixed carbon 8 - 12% | K₂O+Na₂O 7.75% | TFe 43.47% |
| Concentrate index | Fixed carbon 92.3% | K₂O+Na₂O 12.73% | TFe 68.93% |
| Recovery rate | 0.8791 | Feldspar recovery rate ≥85% | Iron recovery rate 69.32% |
| Technology highlights | Wet screening and purification of high carbon graphite | Fluorine-free flotation environmentally friendly process | Magnetic separation-flotation combined desulfurization |
6. Core Advantages
High-efficiency and energy-saving design
Ultra-large flotation machine (single tank volume 320m³), energy consumption reduced by 25%.
Closed-circuit regrinding of medium ore, over-grinding rate reduced by 40%.
Environmental compliance
Wastewater recycling rate ≥ 90%, COD discharge ≤ 50mg/L
Tailing dry discharge system (water content ≤ 15%)
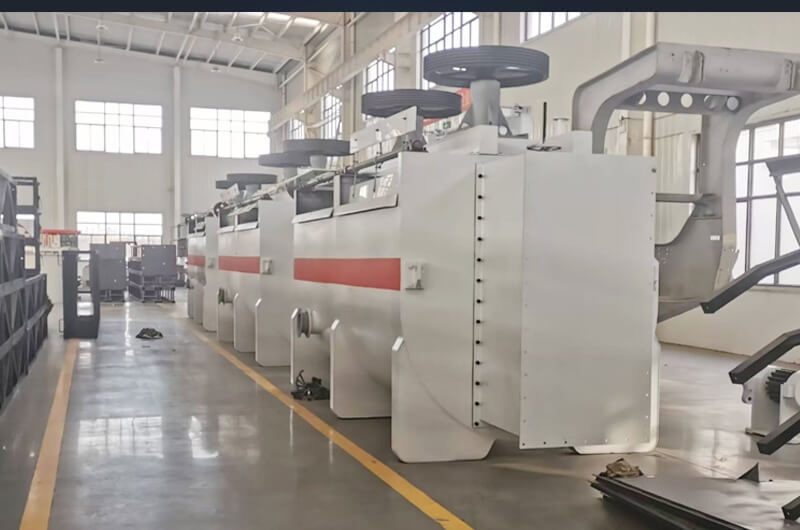

7. Selection and Service
Process design principles
Coarse particle embedding: stage grinding and flotation + rapid flotation (shortening residence time).
Fine particle embedding: selective flocculation + carrier flotation.
Customized service
Laboratory optional test: Provide 50-500kg mineral flotation test.
EPC general package: Covering process design-equipment installation-reagent formula optimization.
Value-added solutions
Comprehensive utilization of tailings: extracting valuable elements or preparing building materials.
Zero-emission system: integrating water treatment and tailings resource modules.




 English
English
 中文
中文