Case study of magnetic separation production line of Chifeng iron ore in Inner Mongolia
In the early stage of cooperation, the ZOOMJO GROUP technical team conducted in-depth field surveys in our mining area, combined with the characteristics of iron ore and production needs, customized an intelligent magnetic separation production line solution, and was responsible for equipment selection, construction and installation, and commissioning guidance throughout the process. Since the production line was put into production in 2021, it has been running stably for more than 3 years, with an equipment failure rate of less than 1%, and the concentrate output and quality have exceeded expectations. Especially in high-cold environments, the low-temperature resistant design and energy-saving performance of ZOOMJO GROUP equipment are particularly outstanding, and the annual comprehensive operating cost is reduced by 15%, truly realizing the promise of "high efficiency, stability, and low consumption".

Customer feedback
In the early stage of cooperation, the ZOOMJO GROUP technical team conducted in-depth field surveys in our mining area, combined with the characteristics of iron ore and production needs, customized an intelligent magnetic separation production line solution, and was responsible for equipment selection, construction and installation, and commissioning guidance throughout the process. Since the production line was put into production in 2021, it has been running stably for more than 3 years, with an equipment failure rate of less than 1%, and the concentrate output and quality have exceeded expectations. Especially in high-cold environments, the low-temperature resistant design and energy-saving performance of ZOOMJO GROUP equipment are particularly outstanding, and the annual comprehensive operating cost is reduced by 15%, truly realizing the promise of "high efficiency, stability, and low consumption".

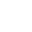
Production line process
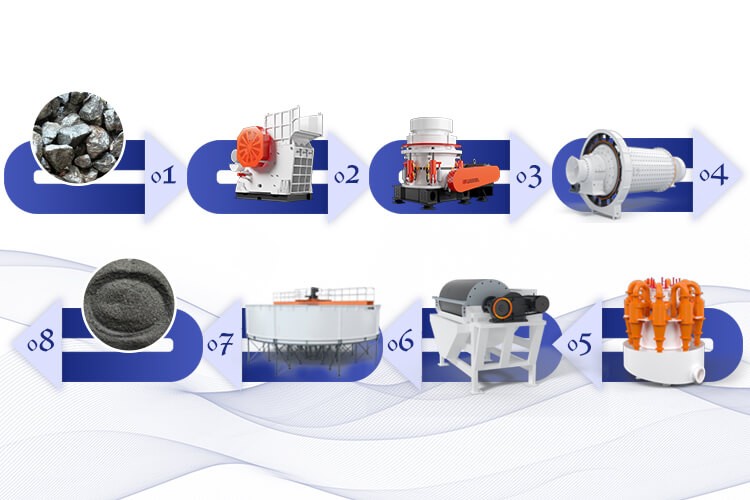

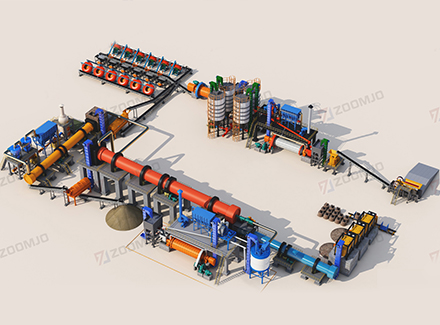
1. Crushing stage
Rough crushing: After blasting and mining, the raw ore is evenly transported to the jaw crusher (C6X series) by a heavy-duty vibrating feeder and crushed to ≤150mm.
Medium and fine crushing: The coarse crushed product enters the multi-cylinder hydraulic cone crusher (HPT300) for secondary crushing, and the particle size is controlled to ≤25mm, which improves the subsequent grinding efficiency.
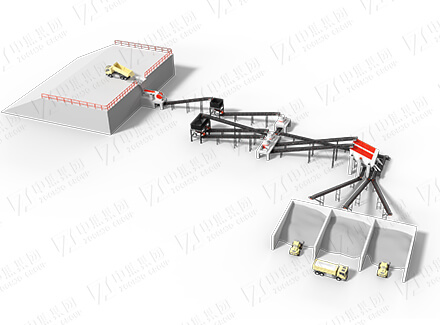
2. Grinding and Classification
Closed-circuit grinding: The crushed iron ore enters a large energy-saving ball mill (MQY3660) for wet grinding, and is matched with a high-frequency vibrating screen and a hydrocyclone to form a closed-circuit system to ensure that the grinding fineness reaches -200 mesh and accounts for ≥85%.
Classification optimization: Unqualified particles automatically return to the ball mill for cyclic grinding, and qualified slurry enters the magnetic separation stage.

3. Multi-stage magnetic separation
Roughing: The pulp is preliminarily magnetically separated by a permanent magnetic drum magnetic separator (CTB1230), and more than 60% of magnetic minerals are separated.
Concentration and scavenging: The coarse concentrate enters the high gradient magnetic separator (SLon-2000) for secondary concentrating, and the tailings are scavenged by the tailings recovery machine, and the comprehensive recovery rate is increased to 93%.
Flotation auxiliary: For silicon-containing impurities, flotation columns (XCF/KYF series) are added for reverse flotation, and the silicon content of the concentrate is reduced to less than 4%.
4. Concentrate dehydration
Concentration and precipitation: The concentrate pulp after magnetic separation enters the high-efficiency deep cone concentrator (NZSG-30), and the underflow concentration is increased to 65%.
Combined dehydration: The concentrated pulp is pre-dehydrated by a ceramic filter (TT-45) and then deeply dried by a gas-fired rotary dryer (Φ3.2×25m). The moisture content of the finished iron ore concentrate powder is ≤9%, and the grade is stable at more than 67%.

Economic Benefits
Capacity improvement: annual processing capacity exceeded 600,000 tons, and concentrate output increased by 35% year-on-year compared with the old line.
Cost optimization: energy consumption per ton of ore decreased by 22%, and labor costs decreased by 40%.
Market competitiveness: the concentrate grade reached the domestic advanced level (TFe ≥ 67%), and the product premium rate increased by 10%.
Through this project, ZOOMJO GROUP once again verified its technological leadership in the field of complex iron ore beneficiation, providing a reliable model for the development of mineral resources in high-altitude and cold regions.



 English
English
 中文
中文